EUR/USD declines after comments from de Galhau
- EUR/USD erases earlier gains after Banque de France chief says ECB should cut at next meeting.
- The pair had been recovering after Lagarde said “game is not over” with inflation.
- Slow economic growth and sticky inflation in the Eurozone could weigh on EUR/USD.
- Federal Reserve Chairman Powell talks about keeping rates higher for longer, and longer.

EUR/USD erases earlier gains and sinks into the 1.0640s on Thursday after Banque de France head and European Central Bank (ECB) policymaker Francois Villeroy de Galhau said, bar a major suprise "we should cut rates at the next meeting."
The next meeting is in May and his comments indicate that he for one wishes to cut interest rates even before the June meeting currently earmarked as the time when most commentators expect the ECB to lower rates. Lower interest rates tend to depreciate a currency as they reduce foreign capital inflows.
De Galhau said there was a risk the ECB might be too late to stave off an economic slowdown if it waited too long before lowering interest rates.
"The risk would be to be behind the curve and to pay a too high cost in terms of economic activity," he added.
EUR/USD rebound stalls
EUR/USD unwound earlier gains made on the back of comments by European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde, who said at a speech in Washington late on Wednesday that “The game (of fighting inflation) is not over,” despite adding, “Growth in Europe is mediocre, much slower than in the US. We’re clearly seeing timid signs of recovery.”
Lagarde’s comments introduced a smidgen of doubt into whether the ECB really will start cutting interest rates in June as markets believe.
Her remark about “Growth in Europe is mediocre,” echoes the view of Rabobank FX Strategists, who argue that whilst there is no risk of a “crisis” in the region, “ the combination of slow growth in the Eurozone and nagging budget pressures could lower the defenses of the EUR going forward." Rabobank suggests a fall to 1.0500 is probable, with risks tilted to the downside.
EUR/USD pressured by talk of higher rates for longer in the US
EUR/USD plummeted at the start of April as bets the Federal Reserve (Fed) would cut interest rates in June quickly melted away amidst stickier-than-expected inflation and robust macroeconomic data.
On Tuesday, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell said high interest rates would likely be around for longer than previously expected given the little progress being made on inflation in recent months.
The Fed’s Beige Book, a comprehensive economic survey, on Tuesday repeated the view that little progress had been made on inflation but added that growth and employment were a little stronger than expected.
Everything points to the Fed maintaining interest rates at their relatively high (upper limit of 5.5% for the Fed Funds Rate) levels for a while until the behemoth of inflation is finally slain.
Indeed, The CME FedWatch tool, a market gauge of the probability of Fed rate cuts, is showing only a 16% probability of a cut in June (from over 70% only a few weeks ago) whilst the odds of a cut by September are now around 70%.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD undertakes a youthful recovery
EUR/USD has undergone a volte-face after hitting a floor at 1.0601 on Tuesday (circled). The question now, as most technical questions are, is whether this is a reversal or just a pullback in an ongoing downtrend?
EUR/USD Daily Chart
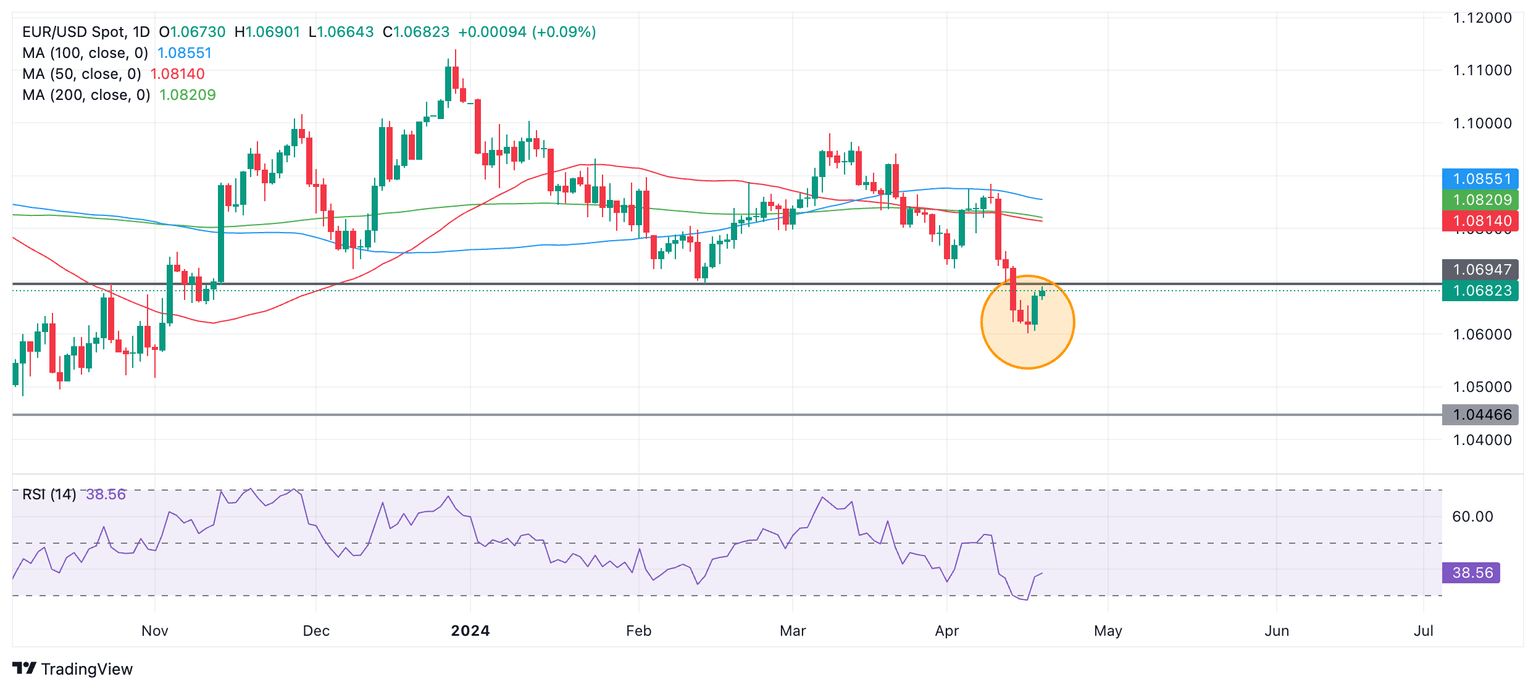
Momentum has been strong in the short span of the recovery so far, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) has moved out of oversold, giving a buy signal – another good sign. However, it is too early to draw conclusions.
The intermediate-term downtrend is probably still in force and in the absence of further proof of a reversal, likely to resume and push the exchange rate lower again.
Resistance from previous swing lows nearby at around 1.0700 could act as an obstacle to the recovery and see a rotation back down. The level will, in any case, offer technical resistance and provide a rallying point for bears even if their cause is doomed.
A break below the 1.0601 April lows would post a lower low and indicate a continuation of the downtrend. After that, the next concrete target is at 1.0446, the October 2023 low.
ECB FAQs
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for the region. The ECB primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the ECB prints Euros and uses them to buy assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Euro. QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The ECB used it during the Great Financial Crisis in 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the covid pandemic.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the European Central Bank (ECB) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the ECB stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Euro.
Author

Joaquin Monfort
FXStreet
Joaquin Monfort is a financial writer and analyst with over 10 years experience writing about financial markets and alt data. He holds a degree in Anthropology from London University and a Diploma in Technical analysis.

















