Most asked questions on US Elections
What happened in the 2024 election?
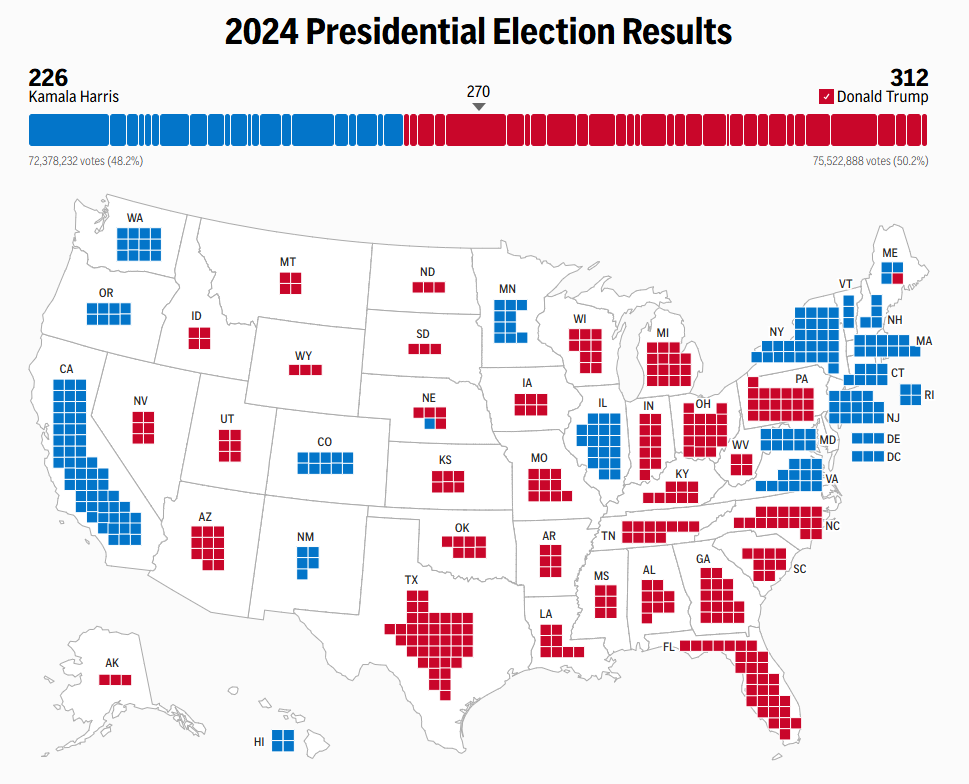
The 2024 United States presidential election concluded with the Republican candidate Donald Trump winning his second non-consecutive term, defeating the Democrat candidate Kamala Harris. Trump secured 312 electoral votes to Harris's 226. Republicans regained control of the Senate and also kept the majority in the House of Representatives.
How are the candidates chosen?
In the United States, presidential elections are usually contested between the two main political parties: the Republican party and the Democratic party. Each party nominates a presidential candidate through a series of state primaries and/or caucuses. There are differences between the parties, a process that can differ fromstate to state.
One of the biggest polling days during this process is known as Super Tuesday, so-called by the fact that more than a dozen states hold their primary contests on that day. The results on Super Tuesday are therefore a strong indicator of the likely eventual presidential nominee of each political party.
How does the US presidential election work?
Candidates compete for 538 electoral college votes, with 270 needed to win. Each state's electoral votes, based partly on population, are won by the candidate who wins the most votes in that state. The winner-takes-all rule applies in most states, meaning the leading candidate receives all that state's electoral votes. Since most states lean toward one party, attention focuses on battleground states, where the outcome is less predictable.
Who can vote?
US citizens aged 18 or older are eligible to vote in the presidential election, which is held every four years.
Why are general elections held on Tuesday after the first Monday in November?
Election Day is strategically scheduled about a month before the Electoral College vote to avoid conflicts with the harvest and harsh weather in agrarian societies. Voting on Tuesday instead of Monday accommodated those traveling to vote, especially from remote areas, as Sunday was typically reserved for religious observance. By choosing the first Tuesday after the first Monday, lawmakers ensured Election Day never coincides with November 1, a date traditionally used by merchants to tally monthly accounts.
What is the lame-duck period?
The period between the election and the inauguration is known as the "lame duck period". During this period, the outgoing president transitions power to the president-elect.