The emerging market currency collapse can continue

Summary
Over the last few months, emerging market currencies have come under extreme pressure. A more hawkish Fed combined with deteriorating global growth prospects have been the root causes of the widespread selloff across the emerging currency complex. While we have a particularly pessimistic view on emerging market currencies, the depreciation has been more severe than we expected. In our view, this depreciation pressure is likely to continue; however, we have consistently been asked "how much more depreciation can EM currencies experience?"
To offer insight, we updated our emerging market currency vulnerability framework and use the results to gauge the extent of further depreciation. The results are compelling, and suggest that underlying economic fundamentals and local politics are consistent with additional weakness in most developing currencies. There are exceptions, however, and our framework suggests fundamentals are consistent with a modest rebound in the Chilean peso, while the politically driven Colombian peso depreciation has likely run its course.
Emerging market currencies have become more vulnerable
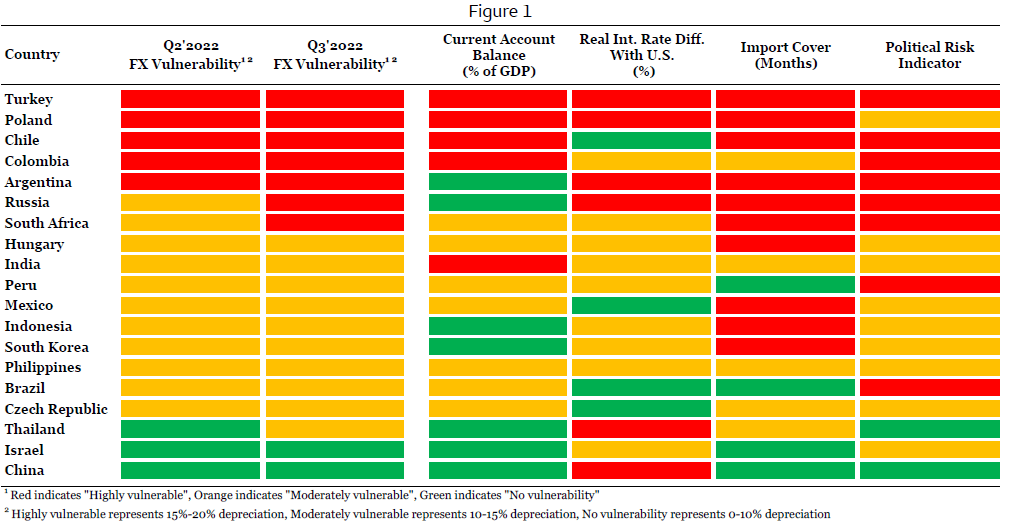
As economists, our responsibilities include proactively recognizing where economic fundamentals and local politics are trending in less or more positive directions. Early identification of these developments can help us make timely adjustments to our forecasts and recommend an appropriate course of action for clients exposed to these countries. Over the years, we have developed and refined tools to help us detect these developments. When we are analyzing emerging market currencies, especially when they have come under broad pressure the way they have this year, we tend to update and utilize our Emerging Markets FX Vulnerability framework quite often. Our vulnerability framework gives us a forward-looking view into how economies and politics are evolving, and supports our effort to be as early as possible in recognizing changing economic and political conditions. Our framework includes a rolling 1-year ahead current account balance forecast and a forward-looking measure of where inflation-adjusted interest rate differentials relative to the U.S. could be in 12 months time. In addition, we include foreign exchange reserve adequacy (import cover) and overlay these data with forward-looking judgment, as well as a political risk indicator which we also apply judgment to where necessary. We add up these variables to get an overall sense of where local conditions are evolving in each developing country we forecast. Currencies associated with eroding fundamentals and politics are typically more vulnerable and volatile, while currencies with stable politics and relatively strong underlying economics can be more protected in an environment where risk assets are performing particularly poorly.
In our view, markets are still in the risk-off environment that has permeated across the globe this year. This global risk off episode is also where our EM FX vulnerability framework works best. In that sense, we updated our vulnerability analysis for Q3-2022 in an effort to assess if and where conditions are evolving, and which currencies could be more or less sensitive. Our latest update reveals interesting conclusions. Our framework suggests that conditions in most countries are stable relative to Q2-2022; however, our analysis reveals that conditions in certain emerging market countries are evolving in a way where currencies are becoming more vulnerable to market shocks. To that point, the Russian ruble and South African rand have become "highly vulnerable" currencies, while conditions in Thailand have deteriorated to the point where the baht is now a "moderately vulnerable" currency (Figure 1). Including Russia and South Africa, conditions in seven countries have evolved in a way that is consistent with outsized depreciations in their respective currencies over the course of a global risk-off event. Including Thailand, ten currencies now fall into the moderately vulnerable segment, while only Israel and China have currencies our framework identify as having little vulnerability.
The ruble's downgrade comes from a lower real interest rate differential with the United States. Given the ruble's capital controls-driven rally and the downward trajectory of local inflation, the Central Bank of Russia (CBR) has started unwinding emergency policy rate hikes from earlier in the year. Over the last few months, the CBR has lowered its Key Rate 1,050 bps to 9.50%. This aggressive easing comes against higher policy rates in the United States, and has diminished the ruble's yield advantage over the U.S. dollar. While a diminished real interest rate differential is driving the ruble's move into the highly vulnerable segment, a reduced yield benefit of the ruble is combined with elevated political risk amid tensions with Western countries and the conflict in Ukraine. In addition, international sanctions restrict CBR access to a majority of its foreign exchange reserves as well as significantly limit the ability of Russia's sovereign wealth fund to transact and generate liquidity. Historically, more-than-adequate FX reserves and a large sovereign wealth fund have acted as pillars of support for the ruble; however, limited buffers has raised the country risk profile of Russia and contribute to the ruble now being a highly vulnerable currency. As of now, Russia's current account surplus prevents the ruble from being the most vulnerable emerging market currency; however, a negative real interest rate differential due to diverging paths for monetary policy between the CBR and the Fed, limited access to buffers and elevated political risk leave the ruble highly sensitive to a large depreciation in times of global market stress.
For the South African rand, we expect the current account surplus to flip into deficit, which is behind the currency's shift into the highly vulnerable segment. With the risk of global recession rising, demand for commodities is likely to ease over the medium term. In fact, we have seen these dynamics play out over the last few weeks as copper prices have plummeted and oil prices have dropped below $100 per barrel on recession risks. Given South Africa is a major commodity exporter, particularly of precious metals and agriculture products, lower demand should result in metals and agriculture prices softening over the medium term. As commodity prices come down, South Africa's current account balance should move out of surplus and into modest deficit. A current account deficit will likely be matched by persistent elevated political risk stemming from insufficient governance controls and little momentum behind implementing a much-needed reform agenda. In addition, the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) has inadequate FX reserves and may struggle to defend the value of the rand in times of extreme volatility. SARB is also likely to maintain only a slim positive real interest rate differential against the United States as policymakers have taken a more gradual approach to interest rate hikes relative to the Fed, while local inflation is likely to continue to trend higher. Altogether, fragile fundamentals and elevated political risks have resulted in the rand returning to a highly vulnerable currency susceptible to a large depreciation in a global risk off scenario.
And in Thailand, the baht's move to moderately vulnerable is driven by the currency now being associated with a negative real interest differential. Bank of Thailand (BOT) policymakers have been an outlier to the higher interest rate trend. Despite inflation trending toward levels last seen during the 2008-2009 Global Financial Crisis and the Asian Financial Crisis of the late 1990's, BOT policymakers have maintained a view that current inflation is only temporary. With a view that price pressures are transitory, the BOT has resisted raising interest rates or engaging in operations consistent with tighter monetary policy. With local inflation spiking, BOT policymakers on hold, and the Fed lifting policy rates quickly, real interest rate differentials have moved into negative territory and are now a source of potential stress on the baht. Aside from diverging paths for monetary policy between the BOT and Fed, underlying fundamentals in Thailand are actually quite strong. The country is likely to maintain a healthy current account surplus of around 1.5% of GDP in 2023, while BOT FX reserves are likely to remain adequate going forward. On the political side, local protests touched off over the last few years in response to COVID-related lockdowns; however, demonstrations did little to disrupt Thailand's political structure, policymaking abilities or governance controls. In that sense, we believe political risk in Thailand is low, and political stability should act as a source of support for the baht in times of global market stress. In aggregate, our framework identifies the economic and political mix in Thailand as consistent with a currency that can now come under more pressure than previously.
Author

Wells Fargo Research Team
Wells Fargo