Federal government runs another deficit despite record revenue

The federal government's budget deficit was “only” $21.93 billion in January.
That was a significant improvement over the $129 billion shortfall recorded in December.
But don’t throw the confetti.
The smaller deficit was primarily due to increased government receipts thanks to a big drop in tax refunds. But the Biden administration is still spending like a drunken sailor. (No disrespect to drunken sailors.)
Meanwhile, interest payments on the rapidly ballooning national debt continue to expand at breakneck speed.
Through the first four months of fiscal 2024, the federal government ran a $531.86 trillion deficit, according to the latest Monthly Treasury Statement. That is a 16 percent increase over the same period in fiscal 2023.
These massive monthly budget shortfalls are pushing the national debt higher at a dizzying pace. On December 29, the national debt eclipsed $34 trillion for the first time. When Congress effectively eliminated the debt ceiling on June 5, the national debt stood at a "mere" $31.46 trillion. As of Feb. 9, the national debt stood at $34.2 trillion.
According to the CBO, debt held by the public is projected to balloon from $26.2 trillion to $48.3 trillion by the end of 2034. That would represent 116 percent of GDP and would be the highest level on record.
The US government has a spending problem
The federal government is a little like a drunk dude up late shopping on Amazon.
The Treasury reported $477.32 billion in receipts last month, a January record. Collection of payroll and income tax withholdings helped boost government revenue. The IRS has also cleared a backlog of delayed income tax filings from the pandemic year.
But even with this revenue windfall, the U.S. government still ran a deficit. That’s because it is addicted to spending money.
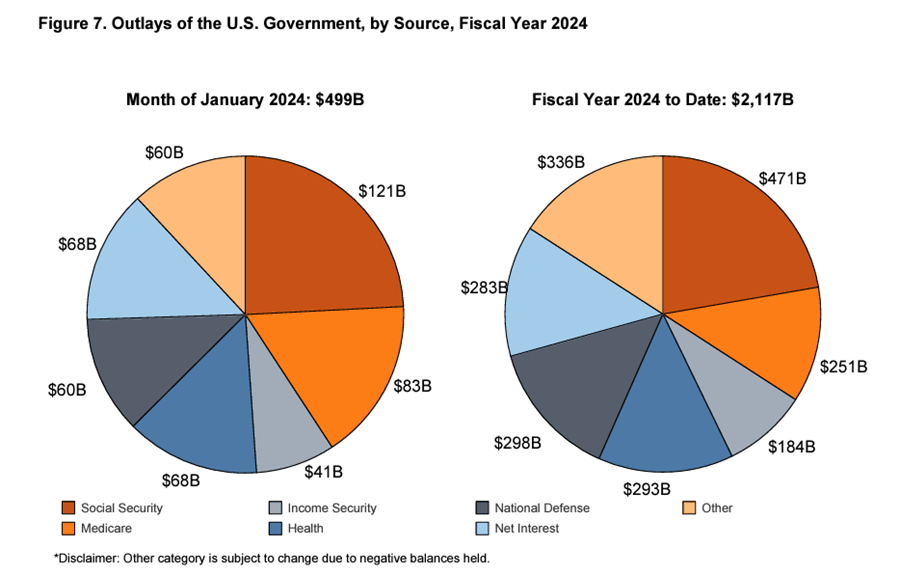
In January, the U.S. Biden administration blew through $499.25 billion, also a January record.
Spending was up 2.7 percent over January 2023, even without any one-time outlays. Last year, January spending was boosted by a $36 billion bailout of a Teamsters union pension fund. If you factor out that one-time expense, federal spending rose nearly 11 percent year-on-year.
This underscores the fact that the fundamental issue isn’t that the U.S. government doesn’t have enough money. The fundamental problem is that the U.S. government spends too much money. Despite the pretend spending cuts, and promises from the Biden administration that it would save “hundreds of billions” the debt ceiling deal (aka the [misnamed] Fiscal Responsibility Act) didn’t address that problem. No matter what you hear about spending cuts, the federal government always finds new reasons to spend more money.
The interest rate problem
These big budget deficits are happening during a time of sharply rising interest rates. This is a big problem for a government that primarily depends on borrowing to pay its bills, and it is likely one of the reasons that the Federal Reserve is talking about rate cuts. The borrow-and-spend U.S. government can’t function in a high interest-rate environment.
The U.S. government spent $69.2 billion on interest expenses alone in January. This was more than the amount spent on national defense ($60 billion) and more than healthcare ($68 billion).
Interest on the federal debt came in $96 billion higher through the first four months of the fiscal year than in the same period last year. The government has shelled out $357 billion on interest payments in fiscal 2023. The only category with higher spending was Social Security.
Net interest expense, excluding intragovernmental transfers to trust funds, was $283 billion through the first four months of the fiscal year, still nearly as much as the government spent on national defense ($298 billion).
And interest expense will only continue to climb.
Much of the debt currently on the books was financed at very low rates before the Federal Reserve started its hiking cycle. Every month, some of that super-low-yielding paper matures and has to be replaced by bonds yielding much higher rates.
The weighted average interest rate on the government’s outstanding Treasury securities rose to 3.21 percent as of the end of January. That compares with a weighted average rate of 2.43 percent in January 2022.
Rising interest rates drove interest payments to over 35 percent as a percentage of total tax receipts in fiscal 2023. In other words, the government is already paying more than a third of the taxes it collects on interest expense.
And it's only going to get worse unless the Fed quickly ratchets down interest rates.
Interest expense will continue to rise at a rapid rate as more and more Treasuries mature and are replaced by higher-yielding bonds.
The only way out of this fiscal death spiral is significant spending cuts and/or major tax hikes.
To receive free commentary and analysis on the gold and silver markets, click here to be added to the Money Metals news service.
Author

Mike Maharrey
Money Metals Exchange
Mike Maharrey is a journalist and market analyst for MoneyMetals.com with over a decade of experience in precious metals. He holds a BS in accounting from the University of Kentucky and a BA in journalism from the University of South Florida.