Eurozone: Less deficit, a little more room for manoeuvre
- The euro area government deficit decreased in 2024 to -3.1% of GDP.
-
Italy and Greece posted primary surpluses even though their interest costs remain high.
-
The fiscal adjustment that still needs to be provided by the countries whose deficits increased in 2024 (France, Austria, Belgium, Finland) will nevertheless act as a brake on growth in the zone.

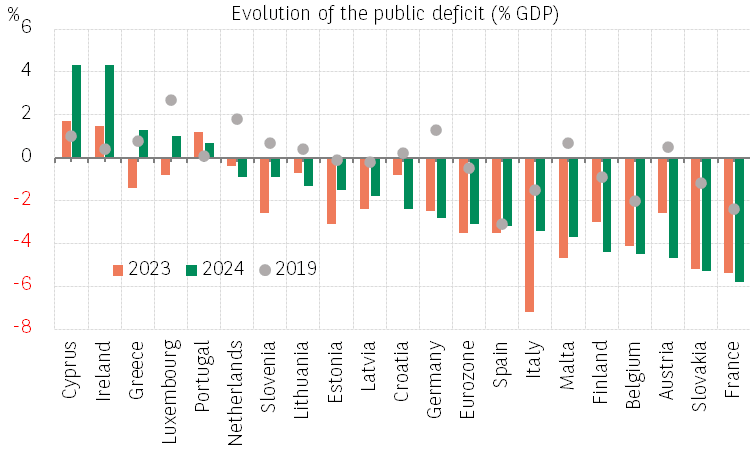
The euro area government deficit decreased by 0.4 pp in 2024 to -3.1% of GDP. The gap compared to the pre-Covid level remains significant (deficit of -0.9% of GDP in 2019). Nevertheless, the improvement in 2024, in a weak economic context (low growth and below potential growth), is remarkable. The primary deficit narrowed from -1.8% to -1.2% of GDP while the debt interest payments rose from 1.7% to 1.9% of GDP, as bond yields rose in 2022-2024.
Half of the countries in the Eurozone recorded a lower deficit last year. One-off effects played a positive role in Italy (reduction of the Superbonus) and Ireland (European fine of EUR15bn paid by GAFAM). Nevertheless, the improvement in public finances of Southern European countries1, supported by still solid economic growth in 2024 (with the exception of Italy), played an important role. The deficit narrowed in Spain (-0.3 pp to -3.2% of GDP), while Greece's deficit (-1.4% in 2023) gave way to a surplus of +1.3% in 2024. While part of this adjustment is therefore cyclical, the structural deficit has also narrowed, according to the IMF's latest estimates2.
Thus, Italy and Greece, which face the highest debt interest payments – as a share of GDP – in the euro area (3.9% and 3.5% respectively), now have primary surpluses (+0.5% and +4.8% of GDP respectively). This allows them to limit the impact of rising financing costs on public debt. In Greece, the public debt ratio decreased by 10 points of GDP to 153.6%. This decline will continue in 2025, with the primary fiscal balance well above the stabilizing threshold3. Nevertheless, the large fiscal adjustment that still needs to be provided by the countries whose deficits increased in 2024 – France (+0.4 percentage points to -5.8%), Austria (+2.1 pp to -4.7%), Belgium (+0.4 pp to -4.5%) and Finland (+1.4 pp to -4.4% of GDP) – will act as a brake on growth in the euro area. However, the latter will benefit from the German recovery plan and European rearmament.
After a slight increase in 2024 (+0.1 pp to 87.4% of GDP), the euro area's public debt-to-GDP ratio could increase more sharply in 2025, given the region's increased financing needs, linked in particular to European rearmament and the likely support of industries affected by the US protectionist offensive, as well as the expected increase in debt interest payments4. Nevertheless, the past improvement in public accounts offers room for manoeuvre to the countries that have made this effort. They are thus better able to absorb the current economic shock and limit tensions on the bond market as much as possible, helped by the ongoing easing of the ECB's monetary policy.
Author

BNP Paribas Team
BNP Paribas
BNP Paribas Economic Research Department is a worldwide function, part of Corporate and Investment Banking, at the service of both the Bank and its customers.